Overview
Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed up recovery. Treatment includes rest, good footwear, heel pads, painkillers, and exercises. A steroid injection or other treatments may be used in more severe cases. Plantar fasciitis means inflammation of your plantar fascia. Your plantar fascia is a strong band of tissue (like a ligament) that stretches from your heel to your middle foot bones. It supports the arch of your foot and also acts as a shock-absorber in your foot.
Causes
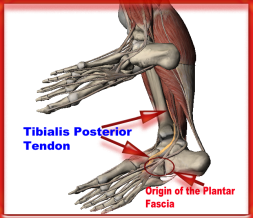
Your plantar fascia (fay-sha) supports the arch of your foot as you run or walk. It is a thick, inelastic, fibrous band that starts in your heel, runs along the bottom of your foot, and spreads out to your toes. Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of this fibrous band. If you are female or have a job that requires a lot of walking or standing on hard surfaces you are more at risk for plantar fasciitis. Additional causes include Being overweight, Having flat feet or high arches, Wearing shoes with poor support, Walking or running for exercise, Tight calf muscles that limit how far you can flex your ankles, Running on soft terrain, Increase in activity level, Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms
Plantar fascia usually causes pain and stiffness on the bottom of your heel although some people have heel spurs and suffer no symptoms at all. Occasionally, heel pain is also associated with other medical disorders such as arthritis (inflammation of the joint), bursitis (inflammation of the tissues around the joint). Those who have symptoms may experience ‘First step’ pain (stone bruise sensation) after getting out of bed or sitting for a period of time. Pain after driving. Pain on the bottom of your heel. Deep aching pain. Pain can be worse when barefoot.
Diagnosis
During the physical exam, your doctor checks for points of tenderness in your foot. The location of your pain can help determine its cause. Usually no tests are necessary. The diagnosis is made based on the history and physical examination. Occasionally your doctor may suggest an X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to make sure your pain isn’t being caused by another problem, such as a stress fracture or a pinched nerve. Sometimes an X-ray shows a spur of bone projecting forward from the heel bone. In the past, these bone spurs were often blamed for heel pain and removed surgically. But many people who have bone spurs on their heels have no heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Although there is no single cure, many treatments can be used to ease pain. In order to treat it effectively for the long-term, the cause of the condition must be corrected as well as treating the symptoms. Rest until it is not painful. It can be very difficult to rest the foot as most people will be on their feet during the day for work. A plantar fasciitis taping technique can help support the foot relieving pain and helping it rest. Plantar fasciitis tapingApply ice or cold therapy to help reduce pain and inflammation. Cold therapy can be applied for 10 minutes every hour if the injury is particularly painful for the first 24 to 48 hours. This can be reduced to 3 times a day as symptoms ease. Plantar fasciitis exercises can be done if pain allows, in particular stretching the fascia is an important part of treatment and prevention. Simply reducing pain and inflammation alone is unlikely to result in long term recovery. The fascia tightens up making the origin at the heel more susceptible to stress. Plantar fasciitis night splint. Plantar fasciitis night splint is an excellent product which is worn overnight and gently stretches the calf muscles preventing it from tightening up overnight.
Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.
Prevention
The following steps will help prevent plantar fasciitis or help keep the condition from getting worse if you already have it. Take care of your feet. Wear shoes with good arch support and heel cushioning. If your work requires you to stand on hard surfaces, stand on a thick rubber mat to reduce stress on your feet. Do exercises to stretch the Achilles tendon at the back of the heel. This is especially important before sports, but it is helpful for non-athletes as well. Ask your doctor about recommendations for a stretching routine. Stay at a healthy weight for your height. Establish good exercise habits. Increase your exercise levels gradually, and wear supportive shoes. If you run, alternate running with other sports that will not cause heel pain. Put on supportive shoes as soon as you get out of bed. Going barefoot or wearing slippers puts stress on your feet. If you feel that work activities caused your heel pain, ask your human resources department for information about different ways of doing your job that will not make your heel pain worse. If you are involved in sports, you may want to consult a sports training specialist for training and conditioning programs to prevent plantar fasciitis from recurring.